
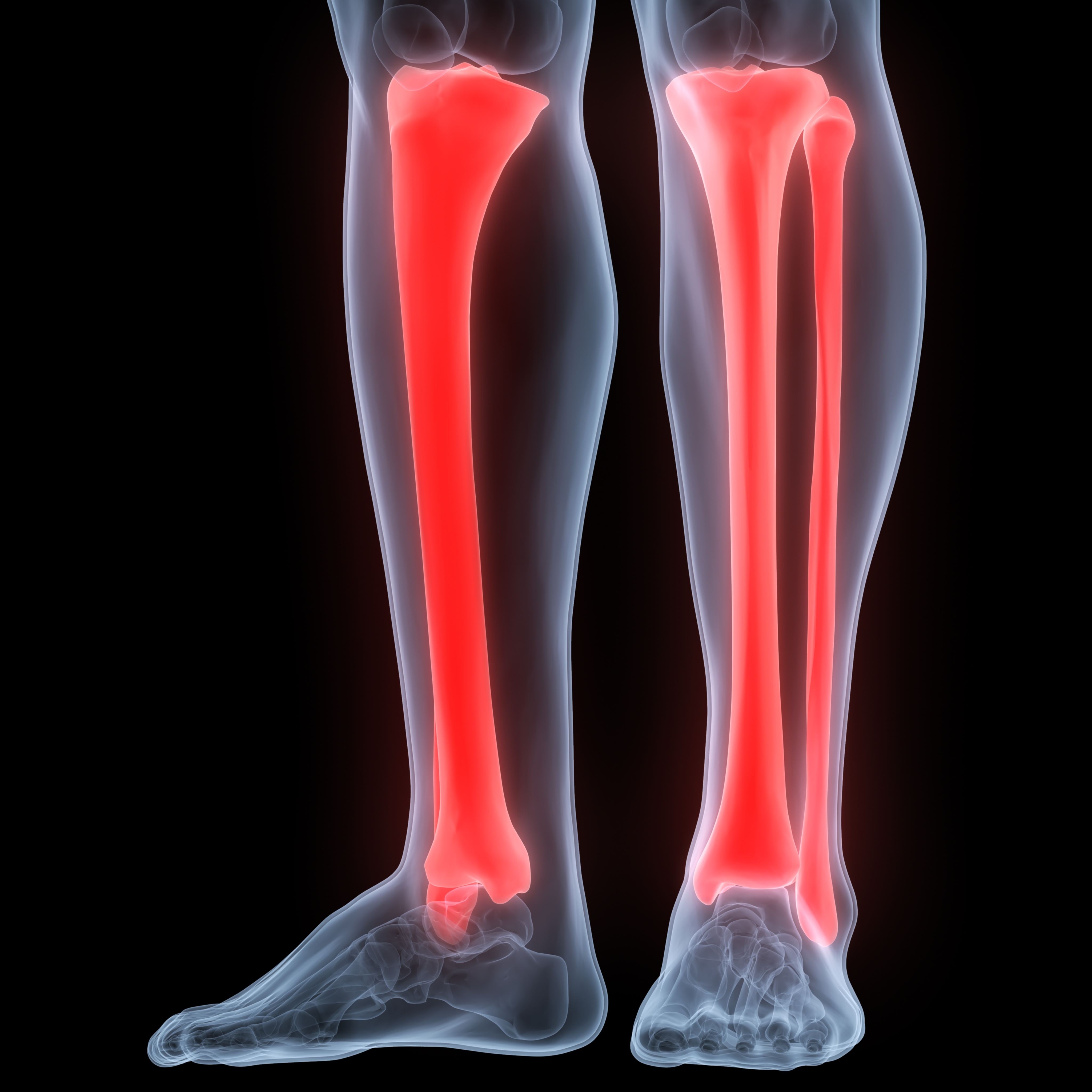
The duration is three to four weeks for toddlers and six to 10 weeks for older children. The treatment typically involves immobilization in a short- or long-leg cast. Examination usually reveals tenderness or swelling at the lower part of the tibia. It can be caused by a mildly traumatic event or a twisting injury. This type of fracture is usually seen in children under four. Nondisplaced: A fracture where the broken bones remain aligned.There are three types of tibial shaft fractures: This type of fracture takes place in the middle, or shaft (diaphysis), of the tibia. Valgus deformity (knock knee) is one of the main potential complications after this fracture. The cast is usually worn for about six weeks. This injury can happen when force is applied to the side of the knee while the leg is extended. It is typically treated by setting the bone without surgery and using a cast to reduce movement. It is most common in children between the ages of two and eight. Proximal Tibial Metaphyseal Fracture (Cozen’s Fracture): This fracture affects the “neck” of the bone (metaphysis), where the tibia starts to narrow down.Treatment usually consists of setting the bone without surgery, which in some cases may be accompanied by surgical insertion of special pins or screws to secure the tibia while it heals. It may affect future growth and cause deformities if not addressed correctly. Separation of the growth plate from the bone is usually caused by direct force to the knee. It’s important to have this type of fracture corrected properly. Proximal Tibial Epiphyseal Fracture: This type of fracture affects the top portion of the bone (epiphysis) and the growth plate.Common proximal tibial fractures include: Depending on the exact location, a proximal tibial fracture may affect the stability of the knee as well as the growth plate. These fractures occur in the knee end of the tibia and are also called tibial plateau fractures. Sometimes they may also involve the fracture of the growth plate (physis) located at each end of the tibia. Below are some of the most common tibia and fibula fractures that occur in children. There are several ways to classify tibia and fibula fractures. Common Types of Tibia and Fibula Fractures Tibia and Fibula Fractures Diagnosisįractures of the tibia and fibula are typically diagnosed through physical examination and X-rays of the lower extremities. High-energy fractures, such as those caused by serious car accidents or major falls, are more common in older children. Low-energy, nondisplaced (aligned) fractures, sometimes called toddler’s fractures, occur from minor falls and twisting injuries. Tibia and fibula fractures are characterized as either low-energy or high-energy. The fibula supports the tibia and helps stabilize the ankle and lower leg muscles. It is the main weight-bearing bone of the two. The tibia is much thicker than the fibula. The tibia is a larger bone on the inside, and the fibula is a smaller bone on the outside. Tibia and fibula are the two long bones located in the lower leg. Treatment for tibia and fibula fractures ranges from casting to surgery, depending on the type and severity of the injury.A physical examination and X-rays are used to diagnose tibia and fibula fractures.Or high-energy - caused by high levels of force, such as a car accident or a fall from a long distance. Fractures can be described as low-energy - caused by twisting or falls from standing height.They account for 10 to 15 percent of all pediatric fractures. Tibia fractures are the most common lower extremity fractures in children.

What You Need to Know About Tibia and Fibula Fractures


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
